Ultrasound Pictures “Renal Infarction”
Clinical manifestations Renal Infarction: Flank pain, hematuria, and proteinuria; fever, leukocytosis; nausea, vomiting. Oliguric renal failure may occur. Hypertension develops several days afterward.
Diagnosis Renal Infarction: Determine the cause of the embolism and thrombosis; should be considered in patients with cardiac arrhythmias x Laboratory findings: Elevated GOT (= AST), LDH (very high), and AP. LDH and AP may also be elevated in the urine.
x Sonography with follow-up scans; ultrasound contrast agents may be used if
needed
x CT with contrast medium
x Angiography is rarely necessary
Sonographic findings Renal Infarction:
x The kidney may appear sonographically normal in the acute stage of a renal
artery embolism, or it may contain a wedge-shaped hypoechoic area whose
apex points toward the renal pelvis.
x Later an echogenic triangular scar develops, causing an indentation of the renal
surface with narrowing of the parenchymal border.
x With a hemorrhagic infarction due to renal artery thrombosis, parenchymal
bleeding leads to an irregular, patchy echogenic area in the renal parenchyma.
x CDS shows an absence of flow in the renal artery and may show a wedgeshaped perfusion defect in the parenchyma.
x Later scans show a decrease in renal size.
Accuracy of sonographic diagnosis Renal Infarction: A fresh infarction cannot be confidently diagnosed without CDS, which has an accuracy rate up to 85%. The diagnosis can be established by using ultrasound contrast agents or CT angiography.
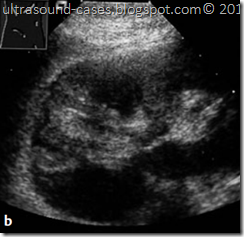
ultrasound images Renal Infarctiona, b Renal infarction. a Wedge-shaped, s harply circumscribed hyperechoic area. b Magnification: The triangular avascular area confirms the infarction. The patient presented clinically with flank pain. For CDS see also Figs.
“Ultrasound cases info Renal Infarction”
“Ultrasound upper abdominal pain”

Posting Komentar untuk "Ultrasound Pictures “Renal Infarction”"