Ultrasound Pictures “Urinary Retention”
Clinical manifestations Urinary Retention: retention of urine, increasing pain in the lower abdomen
Diagnosis Urinary Retention: history (onset of pain, location of pain, last voiding); urinalysis; sonography; urethral catheter
Sonographic findings Urinary Retention:
x Markedly distended bladder
x The renal pelvis is often dilated and anechoic as a result of bladder tamponade
and reflux
x High-level internal echoes (blood clots) may be seen.
Diagnosis Urinary Retention: history (onset of pain, location of pain, last voiding); urinalysis; sonography; urethral catheter
Sonographic findings Urinary Retention:
x Markedly distended bladder
x The renal pelvis is often dilated and anechoic as a result of bladder tamponade
and reflux
x High-level internal echoes (blood clots) may be seen.
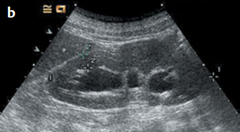
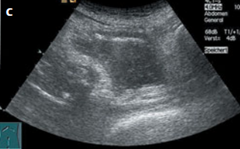
a and c ultrasound cases Urinary retention.
a Strongly distended bladder, tender to pressure, with faint internal echoes
(clotted blood). The patient, taking 300 mg/day of aspirin, presented
clinically with hemorrhagic cystitis.
b Dilated, obstructed, anechoic renal pelvis. c Following bladder irrigation
(to clear blood clots causing bladder tamponade), ultrasound demonstrates
intravesical air (echogenic crescent along the bladder roof). Bright swirling echoes (blood) can be seen during irrigation
a Strongly distended bladder, tender to pressure, with faint internal echoes
(clotted blood). The patient, taking 300 mg/day of aspirin, presented
clinically with hemorrhagic cystitis.
b Dilated, obstructed, anechoic renal pelvis. c Following bladder irrigation
(to clear blood clots causing bladder tamponade), ultrasound demonstrates
intravesical air (echogenic crescent along the bladder roof). Bright swirling echoes (blood) can be seen during irrigation
Technorati Tags: Ultrasound Pictures Urinary Retention

Posting Komentar untuk "Ultrasound Pictures “Urinary Retention”"