Ultrasound Pictures of “Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion”
Clinical manifestations Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion: Colicky pain of very sudden onset, circumscribed and later diffuse. The pain subsides as the condition worsens. Intestinal gangrene develops with peritonitis and abdominal rigidity, sepsis, and shock. Vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, and constipation may occur.
Cause Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion is often cardiogenic: Absolute arrhythmia with atrial fibrillation, dilatative
cardiomyopathy, or a ventricular aneurysm after myocardial infarction.
Course Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion: Embolism develops more rapidly than thrombosis.
Diagnosis Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion:
Laboratory findings: Include acidosis, elevated serum lactate, and leukocytosis
Ultrasound imaging and Doppler sonography of the mesenteric vessels (superior and inferior mesenteric arteries)
Radiography: Contrast enema with a water-soluble contrast medium to check
for edematous thickening (“thumbprinting”) of the bowel wall
Celiacography and mesentericography
Look for the source of the embolus and/or signs of atherosclerosis.
Sonographic findings Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion:
Ultrasound Pictures of Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion Significant, hypoechoic wall thickening affecting a long bowel segment, becoming less pronounced over time
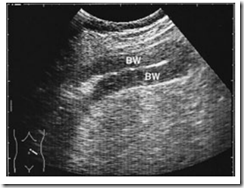
Ultrasound Pictures of Mesenteric infarction: Segmental thickening of hypoechoic bowel wall (BW) with absence of peristalsis. The bowel lumen appears as an echogenic band
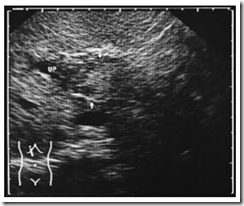
Ultrasound Pictures of Acute portal vein thrombosis. Mass in the portal vein (VP) is isoechoic to liver tissue (arrows). Doppler scanning shows no evidence of flow.
a Ultrasound Pictures of Stenosis of the superior mesenteric artery: Echogenic plaques at the origin of the superior mesenteric artery, initially difficult to identify. b CDS shows bright color pixels (aliasing) indicating turbulence and high flow velocities. c Spectral curve in a pulsed Doppler scan shows flow acceleration to 4 m/s
Acute luminal narrowing, progressing to dilatation due to ischemic malabsorption
x Decreased peristalsis progressing to aperistalsis
x Doppler sonography: atherosclerosis of the mesenteric vessels, occasionally
with demonstrable stenosis of the celiac trunk or superior mesenteric artery
Accuracy of ultrasound diagnosis Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion: Typical ultrasound findings narrow the differential diagnosis, but mesenteric vascular occlusion cannot be diagnosed by exclusion. The definitive diagnosis is made at operation, since an arterial stenotic occlusion and a thrombotic venous occlusion are often indistinguishable by ultrasound.



Posting Komentar untuk "Ultrasound Pictures of “Mesenteric Vascular Occlusion”"