Renal Tract Emergencies
Ultrasound is usually the firstline investigation in the assessment of acute loin
pain, which in the absence of trauma is commonly due to acute urinary tract obstruction and/or renal infection (Fig. Ultrasound images below). Less common acute presentations include renal vein thrombosis or spontaneous haemorrhage, usually from a renal tumour or cyst.
Until recently, ultrasound and/or intravenous urography (IVU) have been the investigations of choice in acute renal colic due to suspected ureteric calculus, and in most UK centres the IVU is currently the method of choice for demonstrating
ureteric obstruction (Fig. ultrasound images below). Low-dose unenhanced multislice CT is increasingly being recommended as a replacement for these two
modalities, but even with this technique diagnostic pitfalls exist. Abdominal ultrasound with or without plain radiography may still provide comparable accuracy where CT resources are limited.
The main limitation of ultrasound in acute ureteric obstruction is that obstruction may be present in the early stages without collecting system dilatation. But the minimally dilated renal pelvis, which would normally be dismissed as unremarkable in a patient with a full bladder, should raise the operator’s suspicion in the patient with acute loin pain. Doppler ultrasound of the kidneys shows a higher resistance index in the obstructed kidney than in the normal side. Upper tract obstruction can be relieved via cystoscopy-guided ureteric stent placement. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous nephrostomy may be required if this is not practicable, or if there is evidence of infection.
Renal infection with parenchymal involvement (acute pyelonephritis) may be the cause of severe acute loin pain with fever, but ultrasound examination mostly shows no abnormality. Occasionally the skilled operator using high-specification equipment may be able to identify segmental areas of high reflectivity, showing decreased blood flow with power Doppler. The diagnosis of this condition is usually based on clinical criteria, but these segments can be demonstrated with CT if necessary.
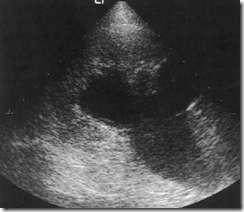
Ultrasound images of Obstructed kidney with pelvicalyceal system (PCS) dilatation and a dilated upper ureter.
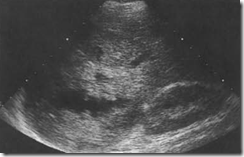
Ultrasound images of Mobile stones were demonstrated in the bladder, but the level of obstruction in the ureter could not be positively identified. Intravenous urogram (IVU) confirmed a stone in the ureter.
Severe laceration to the liver following a road traffic accident.

Posting Komentar untuk "Renal Tract Emergencies"