“ULTRASOUND PICTURES of Splenic Infarction”
Clinical manifestations Splenic Infarction: Sudden onset of left upper quadrant pain
Diagnosis Splenic Infarction:
x History: Underlying disease that may cause thrombosis (e.g., hemoglobinopathy, myeloproliferative disease) or embolism (e.g., cardiac arrhythmia, atherosclerosis, heart disease, or endocarditis)
x Auscultation of a perisplenic friction sound
x Sonography: Clinical manifestations antedate changes on B-mode images. The
infarction can be quickly detected by the use of ultrasound contrast agents
x Splenic scintigraphy
x CT angiography shows a change in the acute stage
x History: Underlying disease that may cause thrombosis (e.g., hemoglobinopathy, myeloproliferative disease) or embolism (e.g., cardiac arrhythmia, atherosclerosis, heart disease, or endocarditis)
x Auscultation of a perisplenic friction sound
x Sonography: Clinical manifestations antedate changes on B-mode images. The
infarction can be quickly detected by the use of ultrasound contrast agents
x Splenic scintigraphy
x CT angiography shows a change in the acute stage
Sonographic findings Splenic Infarction: Same causes and same appearance as a renal infarction
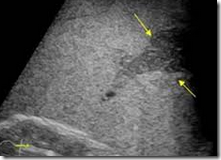
x Fresh: Hypoechoic, superficial parenchymal change, usually wedge-shaped
x Old: Echogenic change with associated surface retraction
x Splenic infarctions may also develop into cystic lesions.
x Fresh: Hypoechoic, superficial parenchymal change, usually wedge-shaped
x Old: Echogenic change with associated surface retraction
x Splenic infarctions may also develop into cystic lesions.
Accuracy of sonographic diagnosis Splenic Infarction: The morphologic changes are easily identified, but it is difficult to make an etiologic diagnosis. Only CDS is rewarding in
the acute stage. The level of diagnostic confidence can be significantly increased
by adding ultrasound contrast agents.
the acute stage. The level of diagnostic confidence can be significantly increased
by adding ultrasound contrast agents.
“Upper abdominal Pain”
“ULTRASOUND PICTURES of Splenic Infarction”
Posting Komentar untuk "“ULTRASOUND PICTURES of Splenic Infarction”"